
Anterograde amnesia is associated with a wide variety of degrees of forgetfulness which can have a devastating impact on the person that suffer from it.
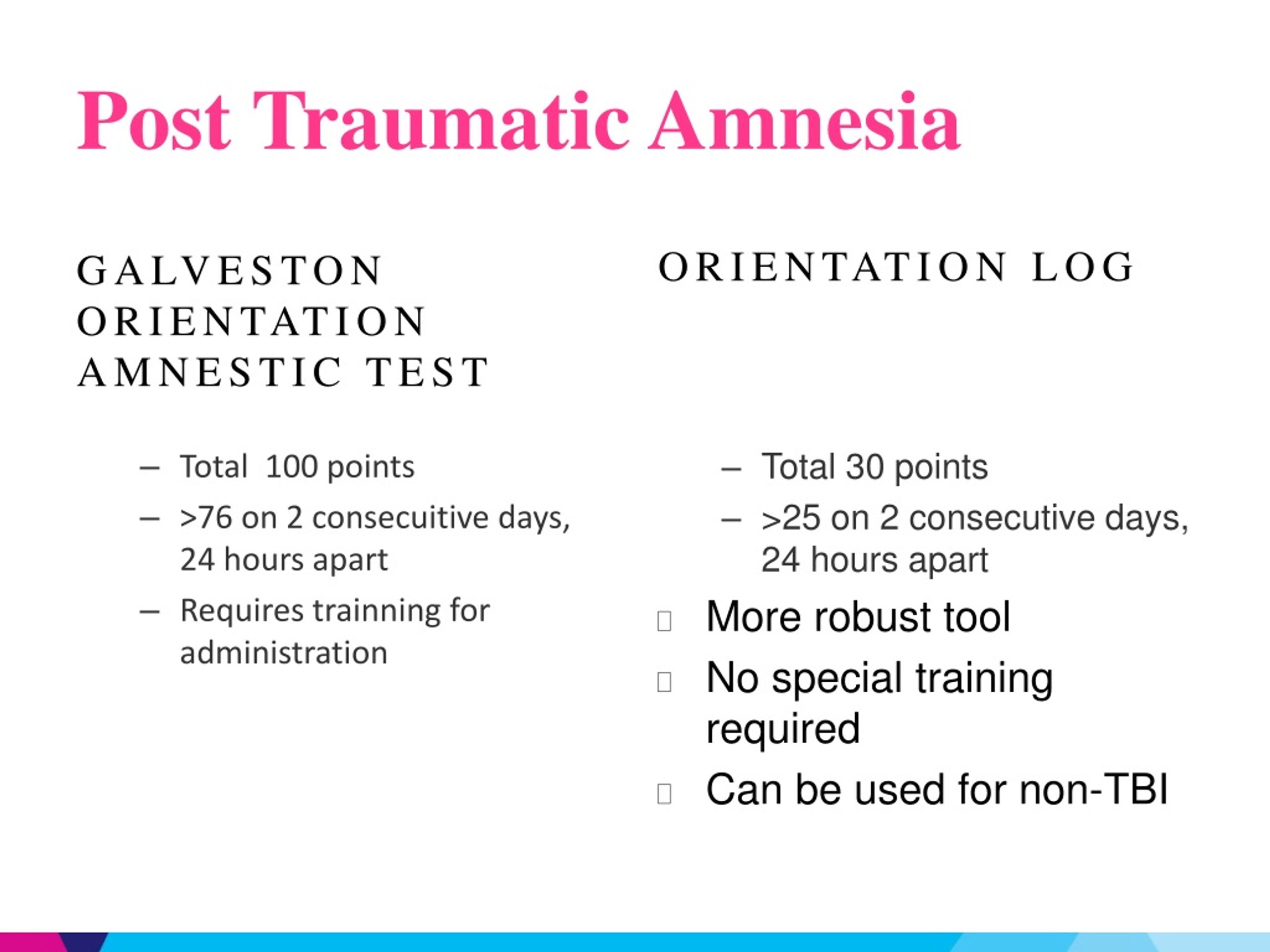
There are two types of PTA: The first one is called retrograde amnesia, which is the loss of memory formed shortly before the traumatic brain injury occurred, while anterograde amnesia is defined as the inability to create new memories or learn new information after the event that caused the brain injury. feeling dazed, disoriented, or confused), and/or (4) Focal neurological deficit(s) which may or may not be transient. The American Congress of Rehabilitation proves the above point by defining mild traumatic brain injury as “A traumatically-induced physiological disruption of brain function, as manifested by at least one of the following: (1) Any period of loss of consciousness (2) Any loss of memory for events immediately before or after the accident, (3) Any alteration in mental state at the time of the accident (e.g. PTA is one of the most common symptoms of a traumatic brain injury. Post-Traumatic Amnesia (PTA), on the other hand, is defined as a state of confusion that may occur immediately after a traumatic injury to the brain. Amaro Law Firm > Blog > Understanding Post Traumatic Amnesia January 19, 2017Īmnesia is defined as the inability to recall information stored in our brain which is also referred to as loss of memory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
